Fitness for Postpartum Women: Nurturing Health and Wellness After Childbirth

Introduction:
The postpartum period, often referred to as the “fourth trimester,” is a transformative time marked by significant physical, emotional, and hormonal changes following childbirth. While caring for a newborn takes center stage during this period, it’s essential for postpartum women to prioritize their own health and well-being, including incorporating fitness into their routine. Engaging in regular exercise not only promotes physical recovery and strength but also supports mental health, energy levels, and overall vitality during the postpartum journey. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the importance of fitness for postpartum women, address common concerns and considerations, and provide practical tips for safely and effectively incorporating exercise into the postpartum lifestyle.
The Importance of Fitness for Postpartum Women:
The postpartum period brings about a myriad of changes in a woman’s body, including hormonal fluctuations, abdominal muscle separation (diastasis recti), pelvic floor weakness, and changes in posture and alignment. Engaging in regular exercise can help address these physical changes, promote recovery, and improve overall strength and fitness levels. Additionally, exercise plays a crucial role in supporting mental health and emotional well-being during the postpartum period, helping to alleviate stress, anxiety, and symptoms of postpartum depression.
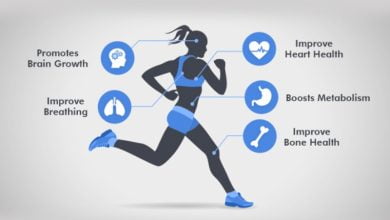
Physical Benefits of Exercise for Postpartum Women:
Promoting Recovery:
Exercise can help accelerate postpartum recovery by improving circulation, reducing inflammation, and promoting tissue healing. Gentle movements and stretches can alleviate discomfort and stiffness commonly experienced after childbirth.
Strengthens Core Muscles:
Targeted exercises can help strengthen the abdominal muscles, including the transverse abdominis and pelvic floor muscles, which may become weakened during pregnancy and childbirth. Strengthening the core muscles is essential for improving posture, stability, and pelvic alignment.
Enhances Cardiovascular Fitness:
Incorporating cardiovascular exercise, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can improve heart health, endurance, and energy levels, which may be depleted during the postpartum period.
Supports Weight Management:
Regular exercise, combined with a balanced diet, can aid in postpartum weight loss and maintenance, helping women achieve their pre-pregnancy weight and body composition goals.
Boosts Mood and Energy:
Exercise releases endorphins, the body’s natural feel-good hormones, which can help alleviate stress, anxiety, and symptoms of postpartum depression. Engaging in physical activity also boosts energy levels and improves overall mood and well-being.
Considerations and Common Concerns:
While exercise is generally safe and beneficial for postpartum women, it’s essential to approach fitness with caution and consideration for individual circumstances and needs. Here are some common considerations and concerns to keep in mind when starting or resuming an exercise routine postpartum:
Consult with Healthcare Provider:
Before starting any postpartum exercise program, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider, such as an obstetrician-gynecologist or midwife, to ensure that it’s safe to do so based on individual health status and any specific medical concerns or complications.
Start Slowly and Progress Gradually:
Ease back into exercise gradually, starting with gentle movements and low-impact activities. Listen to your body and pay attention to how you feel during and after exercise, adjusting intensity and duration as needed.
Be Mindful of Pelvic Floor Health:
Pregnancy and childbirth can weaken the pelvic floor muscles, leading to issues such as urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse. Incorporate pelvic floor exercises, such as Kegels, into your routine to strengthen these muscles and support pelvic health.
Address Diastasis Recti:
Diastasis recti, or separation of the abdominal muscles, is common during pregnancy and may persist postpartum. Avoid exercises that exacerbate diastasis recti, such as traditional crunches and sit-ups, and focus on core-strengthening exercises that engage the deep abdominal muscles.
Stay Hydrated and Nourished:
Adequate hydration and nutrition are essential for supporting postpartum recovery and energy levels. Drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially if breastfeeding, and consume a balanced diet rich in nutrient-dense foods to fuel your body and support overall health.
Listen to Your Body:
Pay attention to any warning signs or discomfort during exercise, such as pain, dizziness, or excessive fatigue, and adjust your routine accordingly. It’s essential to prioritize safety and avoid overexertion, especially in the early postpartum period.
Practical Tips for Postpartum Fitness:
Incorporating exercise into the postpartum lifestyle can be both enjoyable and manageable with the right approach and mindset. Here are some practical tips for postpartum women looking to prioritize fitness:
Start with Gentle Activities:
Begin with gentle activities such as walking, yoga, or swimming, which are low-impact and easy on the body. Gradually incorporate other forms of exercise, such as strength training and aerobic workouts, as you regain strength and endurance.
Include Baby in Workouts:
Get creative and involve your baby in your workouts by using a baby carrier for walks or incorporating them into bodyweight exercises such as squats and lunges. This allows you to bond with your baby while also staying active.
Join Postpartum Exercise Classes:
Consider joining postpartum exercise classes or programs specifically designed for new moms. These classes provide social support, guidance from fitness professionals, and a supportive environment for postpartum women to exercise safely and effectively.
Prioritize Self-Care:
Carve out time for self-care and exercise, even if it’s just a few minutes each day. Remember that taking care of your own health and well-being is essential for your overall happiness and ability to care for your baby.
Set Realistic Goals:
Set realistic and achievable fitness goals based on your individual circumstances and priorities. Focus on progress rather than perfection and celebrate small victories along the way.
Be Patient and Kind to Yourself:
Remember that postpartum recovery takes time, and it’s okay to progress at your own pace. Be patient and kind to yourself, and listen to your body’s cues as you navigate your postpartum fitness journey.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, fitness plays a crucial role in supporting postpartum recovery and promoting overall health and well-being for new moms. By incorporating regular exercise into their routine, postpartum women can strengthen their bodies, boost their energy levels, and enhance their mood and mental well-being during this transformative time. However, it’s essential to approach postpartum fitness with caution and consideration for individual needs and circumstances, consulting with healthcare providers and prioritizing safety and self-care. With the right mindset, support, and guidance, postpartum women can embrace fitness as an integral part of their postpartum journey, nurturing their health and vitality as they navigate the joys and challenges of motherhood.
Promotes Recovery: The Role of Exercise and Self-Care in Healing:
Recovery is a multifaceted journey that encompasses physical, emotional, and psychological healing following illness, injury, or surgery. While the process of recovery is unique to each individual and situation, incorporating exercise and self-care practices can play a pivotal role in promoting healing, restoring function, and enhancing overall well-being. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the significance of promoting recovery, discuss the benefits of exercise and self-care, and provide practical strategies for fostering healing and resilience.
Understanding Recovery:
Recovery is a dynamic and nonlinear process that involves regaining health, function, and vitality after experiencing a setback or challenge. Whether recovering from surgery, illness, injury, or trauma, the journey of recovery unfolds over time, often characterized by ups and downs, setbacks, and breakthroughs. While medical interventions and treatments play a critical role in addressing underlying conditions and symptoms, promoting recovery extends beyond the realm of traditional medicine to encompass holistic approaches that address the physical, emotional, and spiritual aspects of healing.
The Role of Exercise in Recovery:
Exercise is a powerful tool for promoting recovery and enhancing overall well-being during the healing process. Incorporating physical activity into the recovery journey offers a multitude of benefits, including:
Promoting Circulation and Healing:
Exercise stimulates blood flow and circulation, delivering oxygen and nutrients to injured or affected tissues and promoting the healing process. Gentle movements and stretches can alleviate stiffness, reduce inflammation, and improve range of motion, especially following surgery or injury.
Strengthening Muscles and Joints:
Targeted exercises can help strengthen muscles and joints, improve stability and balance, and prevent secondary complications such as muscle atrophy or joint stiffness. Strengthening exercises are particularly beneficial for individuals recovering from orthopedic surgeries, musculoskeletal injuries, or conditions such as arthritis.
Enhancing Mood and Mental Well-Being:
Exercise releases endorphins, the body’s natural feel-good hormones, which can help alleviate stress, anxiety, and symptoms of depression commonly experienced during the recovery process. Engaging in physical activity boosts mood, energy levels, and overall mental well-being, promoting resilience and coping skills.
Supporting Weight Management:
Regular exercise, combined with a balanced diet, can aid in weight management and prevent weight gain or loss during the recovery period. Maintaining a healthy weight supports overall health and reduces the risk of complications associated with obesity or malnutrition.
Improving Functional Capacity:
Exercise improves functional capacity and endurance, enabling individuals to perform activities of daily living more easily and independently. Functional exercises that mimic real-life movements help build strength, flexibility, and coordination, facilitating a smoother transition back to normal activities.
The Importance of Self-Care in Recovery:
In addition to exercise, self-care practices play a crucial role in promoting recovery and nurturing overall well-being. Self-care encompasses a range of activities and strategies that prioritize physical, emotional, and psychological health, empowering individuals to take an active role in their own healing process. Some key components of self-care include:
Rest and Relaxation:
Adequate rest and relaxation are essential for supporting the body’s natural healing processes and conserving energy during recovery. Prioritize quality sleep, take breaks throughout the day, and engage in relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or gentle yoga.
Nutrition and Hydration:
Proper nutrition and hydration are vital for supporting recovery, replenishing essential nutrients, and promoting tissue repair and regeneration. Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, and stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
Stress Management:
Chronic stress can hinder the recovery process and exacerbate symptoms of illness or injury. Practice stress management techniques such as mindfulness, journaling, or spending time in nature to reduce stress levels and promote relaxation.
Social Support:
Surround yourself with supportive friends, family members, and healthcare professionals who can provide encouragement, assistance, and emotional support during the recovery journey. Lean on your support network for practical help with daily tasks, as well as emotional support and companionship.
Mind-Body Practices:
Explore mind-body practices such as meditation, tai chi, or guided imagery, which promote relaxation, stress reduction, and overall well-being. These practices help foster a sense of calm, inner peace, and resilience in the face of challenges.
Practical Strategies for Promoting Recovery:
Incorporating exercise and self-care practices into the recovery journey requires intention, commitment, and a personalized approach tailored to individual needs and circumstances. Here are some practical strategies for promoting recovery and nurturing overall well-being:
Consult with Healthcare Professionals:
Before starting any exercise or self-care program, consult with healthcare professionals to ensure that it’s safe and appropriate based on your specific health condition, medical history, and treatment plan. Seek guidance from physicians, physical therapists, or other healthcare providers who can provide personalized recommendations and guidance.
Start Slowly and Progress Gradually:
Begin with gentle exercises and self-care practices that are appropriate for your current fitness level and physical condition. Gradually increase the intensity, duration, and frequency of exercise as tolerated, listening to your body and respecting any limitations or restrictions.
Set Realistic Goals:
Set realistic and achievable goals for your recovery journey, taking into account your individual circumstances, abilities, and priorities. Focus on small, measurable steps and celebrate progress along the way, no matter how small.
Create a Supportive Environment:
Surround yourself with supportive friends, family members, and healthcare professionals who can provide encouragement, guidance, and practical assistance as needed. Communicate your needs and preferences openly with your support network, and don’t hesitate to ask for help when needed.
Listen to Your Body:
Pay attention to how your body responds to exercise and self-care practices, and adjust your routine accordingly. If you experience pain, discomfort, or worsening symptoms, scale back or modify your activities as needed to avoid exacerbating the issue.
Practice Patience and Persistence:
Recovery is a gradual process that takes time, patience, and persistence. Be kind to yourself and recognize that healing takes time, setbacks are normal, and progress may not always be linear. Stay committed to your recovery goals and trust in your body’s innate ability to heal and restore itself over time.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, promoting recovery involves a holistic approach that addresses physical, emotional, and psychological aspects of healing. Exercise and self-care practices play complementary roles in supporting recovery, enhancing well-being, and fostering resilience during challenging times. By incorporating regular exercise, rest, nutrition, stress management, and social support into the recovery journey, individuals can optimize their healing potential and regain a sense of health, vitality, and resilience. With intention, commitment, and personalized guidance from healthcare professionals, individuals can navigate the recovery process with confidence, compassion, and a steadfast commitment to their own well-being.
Promoting Circulation and Healing: Enhancing Well-Being Through Improved Blood Flow:
Circulation serves as the lifeline of the body, delivering oxygen, nutrients, and immune cells to tissues and organs while removing waste products and toxins. Optimal circulation is essential for maintaining overall health and supporting the body’s natural healing processes. However, factors such as sedentary lifestyles, poor posture, chronic conditions, and injuries can impede circulation, leading to a range of health issues and delaying the healing process. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the significance of promoting circulation and healing, explore the benefits of improved blood flow, and provide practical strategies for enhancing circulation and supporting healing.
Understanding Circulation and Healing:
Circulation refers to the movement of blood through the cardiovascular system, facilitated by the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic system. Blood carries essential nutrients, oxygen, and immune cells to tissues and organs throughout the body, providing nourishment and support for cellular function and growth. Efficient circulation is crucial for maintaining tissue viability, supporting immune function, and facilitating the healing process following injury, surgery, or illness.Healing is a complex biological process that involves multiple stages, including inflammation, tissue repair, and remodeling. Adequate circulation is essential at each stage of the healing process, as it facilitates the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to injured tissues, removes cellular waste products, and supports immune function. Impaired circulation can compromise the healing process, leading to delayed wound healing, increased risk of infection, and other complications.
The Benefits of Improved Blood Flow:
Promoting circulation offers a multitude of benefits for overall health and well-being, including:
Enhanced Oxygen Delivery:
Improved blood flow facilitates the delivery of oxygen-rich blood to tissues and organs, supporting cellular respiration and metabolism. Adequate oxygenation is essential for energy production, tissue repair, and immune function, promoting optimal health and vitality.
Nutrient Delivery and Waste Removal:
Blood carries essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals to cells and tissues, providing the building blocks necessary for tissue repair and regeneration. Efficient circulation also facilitates the removal of metabolic waste products and toxins, helping to maintain cellular health and function.
Supports Immune Function:
The circulatory system plays a vital role in immune function, transporting immune cells, antibodies, and signaling molecules throughout the body to identify and neutralize pathogens, toxins, and foreign invaders. Improved circulation supports immune surveillance and response, enhancing the body’s ability to defend against infection and illness.
Accelerates Healing:
Optimal circulation promotes the timely delivery of oxygen, nutrients, and immune cells to injured or inflamed tissues, accelerating the healing process. Improved blood flow can help reduce inflammation, promote tissue regeneration, and minimize scarring, leading to faster recovery and improved outcomes following injury, surgery, or illness.
Reduces Pain and Discomfort:
Poor circulation can contribute to pain, discomfort, and stiffness in muscles and joints, exacerbating symptoms of conditions such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, and neuropathy. By enhancing blood flow to affected areas, circulation-promoting strategies can help alleviate pain, improve mobility, and enhance overall comfort and well-being.
Practical Strategies for Enhancing Circulation and Supporting Healing:
Incorporating circulation-promoting strategies into daily life can help optimize healing, support overall health, and enhance well-being. Here are some practical strategies for promoting circulation and supporting healing:
Stay Active:
Regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways to promote circulation and enhance overall cardiovascular health. Engage in aerobic exercises such as walking, swimming, cycling, or jogging to get your heart pumping and improve blood flow throughout the body. Incorporate strength training exercises to build muscle mass, improve muscle tone, and support joint health.
Practice Good Posture:
Poor posture can impede circulation and contribute to muscle tension, discomfort, and pain. Maintain good posture throughout the day by sitting, standing, and moving with proper alignment. Use ergonomic furniture and supportive devices, such as lumbar cushions or ergonomic chairs, to support healthy posture and reduce strain on the spine and muscles.
Stretch and Mobilize:
Incorporate stretching and mobility exercises into your daily routine to improve flexibility, range of motion, and circulation. Focus on stretching tight muscles and joints, paying particular attention to areas prone to stiffness or discomfort. Incorporate dynamic movements, such as yoga or tai chi, to promote circulation and relaxation.
Hydrate Adequately:
Drinking plenty of water is essential for maintaining hydration and supporting circulation. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water per day, or more if you’re physically active or exposed to hot or humid conditions. Proper hydration helps maintain blood volume and viscosity, supporting efficient circulation throughout the body.
Massage Therapy:
Massage therapy can help improve circulation, reduce muscle tension, and promote relaxation, aiding in the healing process. Consider incorporating regular massages into your self-care routine to enhance blood flow, alleviate pain, and support overall well-being. Focus on areas of tension or discomfort, using gentle, rhythmic strokes to encourage circulation and lymphatic drainage.
Heat Therapy:
Heat therapy, such as warm compresses, heating pads, or warm baths, can help dilate blood vessels, improve circulation, and alleviate muscle tension and stiffness. Apply heat to areas of discomfort or tension for 15-20 minutes at a time to promote relaxation and facilitate healing.
Elevate Legs:
If you experience swelling or edema in the lower extremities, elevate your legs above heart level to promote venous return and reduce fluid accumulation. Lie down with your legs elevated on pillows or cushions for 15-20 minutes several times a day to improve circulation and alleviate swelling.
Wear Compression Garments:
Compression garments, such as compression socks or stockings, can help improve circulation in the legs and reduce swelling, discomfort, and fatigue. Wear compression garments during periods of prolonged sitting or standing, during travel, or as recommended by healthcare professionals.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, promoting circulation is essential for supporting healing, enhancing overall health, and optimizing well-being. Improved blood flow facilitates the delivery of oxygen, nutrients, and immune cells to tissues and organs, supporting the healing process following injury, surgery, or illness. By incorporating circulation-promoting strategies such as staying active, practicing good posture, stretching, hydrating adequately, and utilizing complementary therapies such as massage and heat therapy, individuals can enhance circulation, alleviate discomfort, and support optimal healing and recovery. With a holistic approach that addresses physical, emotional, and lifestyle factors, individuals can promote circulation, support healing, and nurture overall well-being for a healthier and more vibrant life.