Unlocking the Power of Fitness: A Comprehensive Guide to Harnessing the Mental Health Benefits

Introduction:
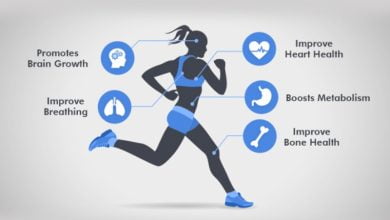
The relationship between physical fitness and mental health is profound and multifaceted. Regular exercise has been shown to have significant benefits for mental well-being, including reducing symptoms of anxiety, depression, and stress, while improving mood, self-esteem, and cognitive function. In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll delve into the powerful connection between fitness and mental health, examining the science behind it, the benefits it offers, and practical strategies for incorporating fitness into your life to promote overall well-being.
Understanding the Science:
The science behind the link between fitness and mental health is complex and multifactorial. Exercise has been found to trigger various physiological and neurochemical changes in the body that positively impact mental health. Some of these changes include:
Neurotransmitter Release:
Exercise stimulates the release of neurotransmitters such as endorphins, serotonin, and dopamine—chemicals in the brain that are known to elevate mood, reduce pain perception, and promote feelings of pleasure and well-being.
Neuroplasticity:
Regular physical activity has been shown to enhance neuroplasticity—the brain’s ability to adapt and rewire itself in response to experiences and stimuli. This can lead to improvements in cognitive function, memory, and emotional regulation, as well as a reduced risk of age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
Stress Reduction:
Exercise acts as a natural stress reliever, helping to reduce levels of cortisol—a hormone associated with stress—and promote relaxation and calmness. Physical activity can also serve as a distraction from daily worries and rumination, allowing individuals to focus on the present moment and experience a sense of flow and mindfulness.
Neurogenesis:
Exercise has been found to stimulate the production of new neurons in the hippocampus—a brain region involved in learning, memory, and emotion regulation. This process, known as neurogenesis, may contribute to improved mood, cognitive function, and resilience to stress and depression.
Sleep Regulation:
Regular exercise can improve sleep quality and duration, which is essential for mental health and overall well-being. Physical activity helps regulate circadian rhythms, reduce insomnia symptoms, and promote deep, restorative sleep, leading to increased energy levels, improved mood, and better mental clarity.
Benefits of Fitness for Mental Health:
Reduced Symptoms of Anxiety and Depression:
Numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of exercise in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression. Regular physical activity has been shown to boost mood, alleviate feelings of sadness and worry, and improve overall emotional well-being.
Stress Management:
Exercise is a natural stress reliever, helping to reduce the physiological and psychological effects of stress on the body and mind. Engaging in physical activity can promote relaxation, increase resilience to stressors, and provide a healthy outlet for pent-up energy and tension.
Improved Self-Esteem and Body Image:
Regular exercise can enhance self-esteem, body image, and self-confidence by promoting feelings of accomplishment, mastery, and empowerment. Physical activity allows individuals to set and achieve fitness goals, build strength and resilience, and cultivate a positive sense of self-worth.
Enhanced Cognitive Function:
Exercise has cognitive-enhancing effects, including improvements in memory, attention, and executive function. Physical activity increases blood flow to the brain, stimulates the release of neurotrophic factors, and promotes neuroplasticity, leading to enhanced cognitive performance and mental acuity.
Social Connection and Support:
Participating in fitness activities can foster social connection, camaraderie, and support, which are essential for mental health and well-being. Group exercise classes, sports teams, and fitness communities provide opportunities for social interaction, friendship, and emotional support, reducing feelings of loneliness and isolation.
Practical Strategies for Incorporating Fitness into Your Routine:
Find Activities You Enjoy:
Choose physical activities and exercises that you genuinely enjoy and look forward to doing. Whether it’s swimming, hiking, dancing, or practicing yoga, find activities that align with your interests, preferences, and fitness goals.
Start Small and Gradually Increase Intensity:
If you’re new to exercise or returning after a hiatus, start with small, manageable goals and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts over time. Focus on building consistency and establishing a regular exercise routine that fits your lifestyle and schedule.
Set SMART Goals:
Set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals to guide your fitness journey and keep you motivated and accountable. Whether it’s running a 5K, mastering a new yoga pose, or increasing the weight you lift, set goals that are challenging yet attainable and track your progress along the way.
Prioritize Regular Physical Activity:
Make physical activity a priority in your daily routine by scheduling time for exercise and treating it as non-negotiable self-care. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening exercises on two or more days per week.
Mix It Up:
Keep your workouts interesting and engaging by mixing up your routine and trying new activities and exercises. Incorporate a variety of cardiovascular, strength training, flexibility, and balance exercises to target different muscle groups and prevent boredom and plateaus.
Listen to Your Body:
Pay attention to how your body feels during and after exercise, and adjust your workouts as needed to accommodate your energy levels, mood, and physical condition. Be kind to yourself and avoid pushing too hard or overtraining, as this can lead to burnout and injury.
Seek Support and Accountability:
Enlist the support of friends, family members, or fitness buddies to help you stay motivated and accountable to your fitness goals. Consider joining a group exercise class, hiring a personal trainer, or participating in online fitness communities to connect with like-minded individuals and share your journey.
Conclusion:
Fitness is not just about physical strength and endurance—it’s also about mental resilience, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life. By incorporating regular physical activity into your routine and prioritizing your mental health, you can experience the transformative power of fitness to uplift your mood, boost your confidence, and enhance your overall sense of well-being. Whether you’re sweating it out in a group exercise class, hitting the trails for a run, or practicing yoga in your living room, remember that every step you take towards better fitness is a step towards better mental health.
Neurotransmitter Release: Unraveling the Intricacies of Neural Communication
In the intricate dance of the human brain, neurotransmitter release serves as the choreographer, orchestrating the symphony of neural communication. From the simplest reflex to the most complex thought processes, neurotransmitter release lies at the heart of every interaction within the nervous system. This phenomenon, which occurs at the synapse—the junction between two neurons—plays a pivotal role in shaping our perceptions, emotions, movements, and memories. To truly grasp the marvels of neurotransmitter release, one must delve into its mechanisms, regulation, and significance in both health and disease.
Mechanisms of Neurotransmitter Release:
The process of neurotransmitter release is a marvel of biological engineering, involving a series of finely tuned molecular events. It begins with the arrival of an action potential, an electrical signal, at the presynaptic terminal of a neuron. This depolarization triggers the opening of voltage-gated calcium channels, allowing calcium ions to rush into the terminal.The influx of calcium serves as the catalyst for exocytosis, the process by which neurotransmitter-containing vesicles fuse with the presynaptic membrane and release their cargo into the synaptic cleft. This release is highly regulated, ensuring precise control over the quantity and timing of neurotransmitter release. Once in the synaptic cleft, neurotransmitters diffuse across the gap and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, initiating a cascade of biochemical events that propagate the signal to the next neuron.
Regulation of Neurotransmitter Release:
The exquisite precision of neurotransmitter release is maintained through a variety of regulatory mechanisms. One such mechanism involves the modulation of calcium influx into the presynaptic terminal. Various factors, including the frequency of action potentials and the concentration of neurotransmitters themselves, can influence the activity of voltage-gated calcium channels, fine-tuning the release of neurotransmitters to meet the demands of neuronal communication.Additionally, presynaptic inhibition and facilitation, mediated by feedback from the postsynaptic neuron or neighboring interneurons, provide another layer of control over neurotransmitter release. These mechanisms allow for the subtle adjustment of synaptic strength, enabling the nervous system to adapt to changing environmental stimuli and physiological states.
Significance of Neurotransmitter Release:
The significance of neurotransmitter release extends far beyond the realm of basic neurobiology, encompassing a wide array of physiological processes and behaviors. For example, the release of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction is essential for the initiation of muscle contraction, enabling movement and motor coordination. Similarly, the release of dopamine in the mesolimbic pathway plays a central role in reward processing and motivation, influencing behaviors ranging from decision-making to addiction.Moreover, neurotransmitter release underlies higher cognitive functions such as learning and memory. The strengthening or weakening of synaptic connections, known as synaptic plasticity, is thought to be the cellular basis of learning and memory formation. By modulating the release of neurotransmitters and the responsiveness of postsynaptic receptors, the brain is able to encode and store information, shaping our experiences and shaping our identities.
Neurotransmitter Release in Health and Disease:
Dysregulation of neurotransmitter release is implicated in a wide range of neurological and psychiatric disorders. For example, disruptions in the release of serotonin, a neurotransmitter involved in mood regulation, are associated with depression and anxiety disorders. Similarly, abnormalities in the release of dopamine are linked to Parkinson’s disease, schizophrenia, and addiction.Understanding the mechanisms underlying neurotransmitter release has thus become a major focus of research in the field of neuroscience. By elucidating the molecular pathways involved in neurotransmitter release and identifying potential therapeutic targets, scientists aim to develop novel treatments for these debilitating conditions, offering hope for millions of individuals worldwide.
In conclusion,
Neurotransmitter release is a fundamental process that underlies virtually every aspect of neural communication. From the simplest reflex to the most complex cognitive function, neurotransmitter release shapes our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors in profound ways. By unraveling the intricacies of this process, we gain insights into the workings of the human brain and open new avenues for understanding and treating neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Introduction: The Connection Between Fitness and Mental Health
As someone who has always been passionate about fitness, I have long been aware of the incredible benefits it provides for both the body and mind. Over the years, I have personally experienced the transformative power of exercise on my own mental health. In this comprehensive guide, I will delve into the various ways in which fitness can help unlock the potential for improved mental wellbeing. By understanding the connection between fitness and mental health, we can harness these benefits to lead happier and more fulfilling lives.
The Mental Health Benefits of Exercise
Exercise has been proven to have a profound impact on mental health. Regular physical activity releases endorphins, which are known as the “feel-good” hormones. These endorphins not only help to improve mood, but they also act as natural painkillers and reduce stress and anxiety. In addition to endorphin release, exercise increases the production of serotonin and dopamine, which are neurotransmitters that play a crucial role in regulating mood.
How Exercise Affects the Brain
The brain is a complex organ, and exercise has a remarkable influence on its structure and function. Research has shown that engaging in physical activity increases the volume of certain brain regions, such as the hippocampus, which is associated with memory and learning. Exercise also promotes the growth of new neurons, a process known as neurogenesis, which is essential for cognitive function and mental health. Furthermore, exercise improves blood flow to the brain, delivering oxygen and nutrients that support its overall health.
Exercise and Stress Reduction
Stress is a common part of life, and chronic stress can have detrimental effects on mental health. However, exercise has been shown to be a powerful tool for managing stress. When we engage in physical activity, our bodies enter a state of heightened arousal, which helps to dissipate the physical tension and mental strain associated with stress. Additionally, exercise triggers the release of endorphins, which act as natural stress relievers. Regular exercise can also improve our ability to cope with stress by providing a healthy outlet for emotional release.
Exercise and Anxiety Management
Anxiety is a prevalent mental health condition that can significantly impact daily life. Fortunately, exercise has been shown to be an effective strategy for managing anxiety symptoms. Physical activity helps to reduce anxiety by increasing the production of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, which are known to promote feelings of calm and relaxation. Exercise also provides a distraction from anxious thoughts and can help improve sleep, which is often disrupted by anxiety. Incorporating regular exercise into your routine can help alleviate anxiety and promote overall mental wellbeing.
Exercise and Depression Alleviation
Depression is a complex mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While exercise is not a cure for depression, it has been proven to be a valuable tool in alleviating symptoms. Engaging in physical activity releases endorphins, which can help improve mood and reduce feelings of sadness and hopelessness. Exercise also increases the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in regulating mood. Additionally, the social aspect of exercise, such as participating in group fitness classes or team sports, can provide a sense of belonging and support, which is crucial for individuals experiencing depression.
Exercise and Improving Sleep Quality
Sleep is essential for overall health and wellbeing, and exercise plays a vital role in promoting a good night’s sleep. Regular physical activity helps regulate our internal body clock, known as the circadian rhythm, which in turn improves sleep quality. Exercise also helps to reduce anxiety and stress, both of which can interfere with sleep. Engaging in moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, has been shown to have the most significant impact on sleep quality. However, it is important to note that exercising too close to bedtime may have the opposite effect and disrupt sleep, so it is best to finish your workout at least a few hours before bedtime.
Exercise and Boosting Self-Esteem and Confidence
Low self-esteem and confidence can have a negative impact on mental health and overall wellbeing. Exercise can be a powerful tool for boosting self-esteem and confidence. When we engage in physical activity, we set goals, push our limits, and achieve personal milestones. These accomplishments contribute to an increased sense of self-worth and confidence. Exercise also helps to improve body image and body satisfaction, as it can lead to physical changes such as weight loss, muscle gain, and improved overall fitness. By incorporatingexercise into our daily lives, we can cultivate a positive body image and enhance our self-esteem.
Incorporating Exercise into Your Daily Routine
Finding the time and motivation to exercise regularly can be a challenge, but with a few simple strategies, it can become a seamless part of your daily routine. Start by setting realistic goals and gradually increasing the duration and intensity of your workouts. Find activities that you enjoy and that align with your interests and preferences. This could be anything from running, swimming, or dancing to practicing yoga or participating in team sports. Scheduling exercise into your calendar and treating it as a non-negotiable appointment can also help make it a priority in your day. Finally, enlist the support of friends or family members to join you in your fitness journey, as accountability and social support can significantly increase adherence to an exercise regimen.
Finding the Right Type of Exercise for Mental Health Benefits
Not all types of exercise are created equal when it comes to mental health benefits. While any form of physical activity is beneficial, certain types of exercise have been shown to have a more significant impact on mental wellbeing. Aerobic exercise, such as running, cycling, or swimming, is particularly effective in improving mood and reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression. This type of exercise increases heart rate, releases endorphins, and stimulates the production of neurotransmitters that promote feelings of happiness and relaxation. Strength training exercises, such as weightlifting or resistance training, also offer mental health benefits by promoting self-esteem and body confidence. Finding the right combination of aerobic and strength training exercises that you enjoy is key to unlocking the mental health benefits of fitness.
Overcoming Barriers to Exercise for Mental Health
While exercise offers numerous mental health benefits, there may be barriers that prevent individuals from engaging in regular physical activity. Lack of time, energy, or motivation are common obstacles that can be overcome with a few simple strategies. Prioritize exercise by scheduling it into your day and treating it as an essential part of your self-care routine. Break down your workouts into shorter, more manageable sessions if time is a concern. Find activities that you genuinely enjoy and that bring you joy, as this will increase your motivation to participate. Consider seeking social support by joining a fitness class or finding a workout buddy to hold you accountable. Lastly, remember that any form of physical activity, no matter how small, is better than none at all. Every step counts towards improving your mental wellbeing.
Seeking Professional Guidance for Mental Health and Fitness
If you are experiencing significant mental health challenges or have specific concerns related to exercise and mental wellbeing, seeking professional guidance can be incredibly beneficial. Mental health professionals, such as therapists or counselors, can provide support and guidance tailored to your unique needs. They can help you navigate the complexities of mental health and develop strategies for incorporating exercise into your overall treatment plan. Additionally, fitness professionals, such as personal trainers or exercise physiologists, can offer expertise in designing exercise programs that target specific mental health goals. Collaborating with professionals who specialize in both mental health and fitness ensures that you receive comprehensive and individualized care.
Combining Exercise with Other Mental Health Strategies
While exercise alone can have a profound impact on mental health, combining it with other strategies can further enhance its benefits. Practices such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and journaling can complement exercise by promoting relaxation and self-reflection. Engaging in activities that bring you joy, such as hobbies or spending time in nature, can also contribute to improved mental wellbeing. Prioritizing sleep, maintaining a balanced diet, and fostering healthy relationships are additional factors that support overall mental health. By combining exercise with these holistic approaches, you can unlock the full potential of fitness for mental wellbeing.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Power of Fitness for Mental Wellbeing
In this comprehensive guide, we have explored the powerful connection between fitness and mental health. Regular exercise has been shown to have a transformative impact on mental wellbeing, alleviating symptoms of stress, anxiety, and depression, improving sleep quality, boosting self-esteem and confidence, and promoting overall mental wellness. By incorporating exercise into our daily routines, finding the right type of exercise that aligns with our preferences, and overcoming barriers to physical activity, we can unlock the full potential of fitness for mental wellbeing. Remember to seek professional guidance when needed and combine exercise with other mental health strategies for a comprehensive approach to self-care. Let us embark on this journey together and unlock the power of fitness to enhance our mental health and lead happier, healthier lives.
CTA:
Start your fitness journey today and experience the incredible mental health benefits that exercise has to offer.