Physical Activity: An Overview of its Importance, Benefits, and Implementation

Introduction
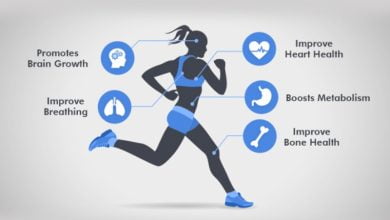
Physical activity, defined as any bodily movement produced by skeletal muscles that requires energy expenditure, is a fundamental aspect of human health and well-being. From reducing the risk of chronic diseases to improving mood and enhancing quality of life, regular physical activity offers a multitude of benefits for individuals of all ages. In this comprehensive overview, we will explore the importance of physical activity, its numerous health benefits, recommended guidelines, and practical strategies for incorporating physical activity into daily life.
Importance of Physical Activity:
Physical activity is essential for maintaining optimal health and preventing various health problems associated with sedentary lifestyles. It plays a crucial role in:
Maintaining Cardiovascular Health:
Regular physical activity strengthens the heart muscle, improves circulation, lowers blood pressure, and reduces the risk of heart disease, stroke, and hypertension.
Maintaining Cardiovascular Health: Strategies for a Strong Heart
Cardiovascular health is paramount to overall well-being, as the heart and circulatory system play vital roles in delivering oxygen and nutrients to every cell in the body. Maintaining cardiovascular health involves adopting lifestyle habits that support optimal heart function and reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the importance of cardiovascular health, factors influencing heart health, strategies for maintaining a healthy heart, and lifestyle changes that promote cardiovascular well-being.
Understanding Cardiovascular Health:
Cardiovascular health refers to the health and function of the heart and blood vessels, encompassing various aspects such as heart rate, blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and overall cardiac function. A healthy cardiovascular system efficiently pumps blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues and organs while removing waste products. Factors that influence cardiovascular health include genetics, lifestyle choices, diet, physical activity, stress levels, and environmental factors.
The Importance of Cardiovascular Health:
Maintaining cardiovascular health is essential for overall health and longevity, as the heart and circulatory system are responsible for sustaining life-sustaining functions. A healthy cardiovascular system:
Reduces the Risk of Heart Disease:
Optimal cardiovascular health lowers the risk of coronary artery disease, heart attack, heart failure, and other heart-related conditions.
Supports Brain Health:
A healthy heart promotes adequate blood flow to the brain, reducing the risk of stroke and cognitive decline.
Enhances Physical Performance:
Improved cardiovascular fitness and endurance support physical performance, allowing individuals to engage in daily activities and exercise with greater ease and efficiency.
Promotes Longevity:
Maintaining cardiovascular health is associated with a longer life expectancy and improved quality of life in older adults.
Strategies for Maintaining Cardiovascular Health:
Adopting lifestyle habits that support cardiovascular health is crucial for preventing heart disease and promoting overall well-being. Some key strategies include:
Healthy Diet:
Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit intake of saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, sodium, and added sugars, which can increase the risk of heart disease.
Regular Exercise:
Engage in regular physical activity, including aerobic exercise, strength training, flexibility, and balance exercises. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days per week.
Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Achieve and maintain a healthy body weight through a combination of balanced nutrition and regular exercise. Excess weight, particularly abdominal obesity, increases the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and other health problems.
Quit Smoking:
Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease and other cardiovascular conditions. Quitting smoking is one of the most important steps individuals can take to improve cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Limit Alcohol Consumption:
Drink alcohol in moderation, if at all. Excessive alcohol consumption can raise blood pressure, triglyceride levels, and the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Manage Stress:
Practice stress-reduction techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, and mindfulness to reduce stress levels and promote relaxation. Chronic stress can contribute to high blood pressure, inflammation, and other cardiovascular risk factors.
Get Quality Sleep:
Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Poor sleep quality and sleep disorders such as sleep apnea are associated with an increased risk of heart disease and other health problems.
Regular Health Check-ups:
Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor blood pressure, cholesterol levels, blood sugar levels, and other cardiovascular risk factors. Early detection and management of risk factors can help prevent heart disease and other cardiovascular conditions.
Conclusion:
Maintaining cardiovascular health is essential for overall health and well-being, as the heart and circulatory system play vital roles in sustaining life-sustaining functions. By adopting lifestyle habits that support optimal heart function, such as eating a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, managing stress, getting quality sleep, and monitoring cardiovascular risk factors, individuals can reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions. Prioritizing cardiovascular health promotes longevity, vitality, and a higher quality of life for years to come.
Promoting Musculoskeletal Health:
Weight-bearing and resistance exercises help build and maintain strong bones, muscles, and joints, reducing the risk of osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, and fractures.
Promoting Musculoskeletal Health: Strategies for Strong Bones, Joints, and Muscles
Musculoskeletal health is integral to overall well-being, as the musculoskeletal system comprises bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, and tendons that provide structure, support, and mobility to the body. Maintaining optimal musculoskeletal health is essential for preventing injuries, supporting physical activity, and promoting independence and mobility throughout life. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the importance of musculoskeletal health, factors influencing musculoskeletal function, strategies for promoting strong bones, joints, and muscles, and lifestyle changes that support musculoskeletal well-being.
Understanding Musculoskeletal Health:
Musculoskeletal health refers to the health and function of the musculoskeletal system, which includes bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, and tendons. This complex system provides structural support, protects vital organs, facilitates movement, and enables activities of daily living. Factors that influence musculoskeletal health include genetics, age, gender, nutrition, physical activity, lifestyle choices, and environmental factors.
The Importance of Musculoskeletal Health:
Maintaining optimal musculoskeletal health is essential for overall health and well-being, as the musculoskeletal system plays numerous roles in the body:
Support and Stability:
The musculoskeletal system provides structural support and stability to the body, maintaining posture and preventing collapse under the force of gravity.
Mobility and Movement:
Joints, muscles, and bones work together to facilitate movement, allowing individuals to perform activities of daily living, exercise, and engage in physical activity.
Protection of Vital Organs:
Bones protect vital organs such as the brain, heart, lungs, and spinal cord from injury and trauma.
Blood Cell Production:
Bones produce red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets in the bone marrow, supporting immune function and oxygen transport throughout the body.
Mineral Storage:
Bones act as a reservoir for essential minerals such as calcium and phosphorus, helping maintain mineral balance in the body.
Strategies for Promoting Musculoskeletal Health:
Adopting lifestyle habits that support musculoskeletal health is crucial for preventing injuries, maintaining mobility, and promoting overall well-being. Some key strategies include:
Nutritious Diet:
Eat a balanced diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, protein, and other essential nutrients that support bone health and muscle function. Include dairy products, leafy greens, nuts, seeds, fish, lean meats, and fortified foods in your diet.
Regular Exercise:
Engage in regular physical activity that includes weight-bearing exercises, resistance training, flexibility exercises, and balance exercises. Weight-bearing exercises such as walking, jogging, dancing, and stair climbing help maintain bone density and strength. Resistance training exercises such as weightlifting, resistance band exercises, and bodyweight exercises help build and maintain muscle mass and strength. Flexibility exercises such as stretching and yoga improve joint range of motion and reduce stiffness. Balance exercises such as Tai Chi and yoga enhance stability and reduce the risk of falls.
Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Achieve and maintain a healthy body weight through a combination of balanced nutrition and regular exercise. Excess weight can increase the load on the musculoskeletal system, leading to joint pain, arthritis, and other health problems.
Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol:
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can negatively impact musculoskeletal health, increasing the risk of osteoporosis, bone fractures, and muscle weakness. Quit smoking and limit alcohol intake to promote musculoskeletal well-being.
Practice Good Posture:
Maintain good posture during daily activities and exercise to reduce strain on the musculoskeletal system. Avoid prolonged sitting or standing in one position and use ergonomic furniture and equipment when possible.
Stay Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support joint lubrication, muscle function, and overall hydration. Dehydration can impair musculoskeletal performance and increase the risk of injury.
Get Adequate Sleep:
Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support muscle recovery, tissue repair, and overall musculoskeletal health. Poor sleep quality and sleep deprivation can impair physical performance and increase the risk of injury.
Manage Stress:
Practice stress-reduction techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and relaxation exercises to reduce muscle tension and promote relaxation. Chronic stress can contribute to muscle pain, tension headaches, and other musculoskeletal problems.
Conclusion:
Promoting musculoskeletal health is essential for overall well-being, as the musculoskeletal system plays vital roles in supporting movement, protecting vital organs, and maintaining structural integrity. By adopting lifestyle habits that support bone health, joint function, and muscle strength, individuals can prevent injuries, maintain mobility, and enhance overall quality of life. Prioritizing musculoskeletal health through proper nutrition, regular exercise, weight management, posture awareness, hydration, sleep hygiene, stress management, and avoiding harmful habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption supports lifelong musculoskeletal well-being and promotes independence and mobility throughout life.
Controlling Weight:
Physical activity helps burn calories, boost metabolism, and maintain a healthy body weight, reducing the risk of obesity and related health problems such as type 2 diabetes and certain cancers.
Enhancing Mental Health:
Exercise releases endorphins, neurotransmitters that improve mood, reduce stress, anxiety, and depression, and enhance cognitive function and overall well-being.
Improving Sleep Quality:
Regular physical activity can improve sleep quality and duration, leading to better overall sleep patterns and daytime alertness.
Boosting Immune Function:
Moderate-intensity physical activity has been shown to enhance immune function, reducing the risk of infections and promoting overall immune health.
Health Benefits of Physical Activity:
The health benefits of regular physical activity are extensive and encompass various aspects of physical, mental, and emotional well-being. Some key benefits include:
Improved Cardiovascular Fitness:
Regular aerobic exercise strengthens the heart and lungs, improves circulation, and enhances cardiovascular fitness and endurance.
Enhanced Muscular Strength and Endurance:
Strength training exercises help build and maintain muscle strength, endurance, and mass, improving overall muscular health and functional capacity.
Increased Flexibility and Mobility:
Flexibility exercises such as stretching and yoga improve joint range of motion, reduce stiffness, and enhance overall flexibility and mobility.
Better Mental Health:
Exercise has been shown to reduce symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress, improve mood, enhance self-esteem, and promote overall mental well-being.
Weight Management:
Physical activity helps control weight by burning calories, increasing metabolism, and preserving lean muscle mass, making it easier to achieve and maintain a healthy body weight.
Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases:
Regular physical activity reduces the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, osteoporosis, and certain cancers.
Recommended Guidelines for Physical Activity:
To reap the health benefits of physical activity, it’s essential to follow recommended guidelines for different age groups. The World Health Organization (WHO) and various health organizations provide guidelines for physical activity, including:
Aerobic Exercise:
Adults should aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week. This can include activities such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, or dancing.
Strength Training
Adults should engage in muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days per week, targeting major muscle groups with exercises such as weightlifting, resistance band exercises, or bodyweight exercises.
Flexibility and Balance Exercises:
Incorporating flexibility and balance exercises into your routine can help improve range of motion, prevent injuries, and enhance overall mobility and stability.
Practical Strategies for Incorporating Physical Activity into Daily Life:
Incorporating physical activity into daily life doesn’t have to be complicated or time-consuming. Simple strategies can help make physical activity a regular part of your routine:
Choose Activities You Enjoy:
Find physical activities that you enjoy and look forward to, whether it’s walking, dancing, swimming, or playing sports. Making exercise fun increases motivation and adherence.
Make It Social:
Exercise with friends, family members, or coworkers to make physical activity more enjoyable and social. Join group fitness classes, sports leagues, or outdoor recreational activities.
Set Realistic Goals:
Set specific, achievable goals for physical activity, such as taking a daily walk, attending a fitness class, or completing a home workout routine. Start small and gradually increase intensity and duration over time.
Incorporate Activity into Daily Routine:
Look for opportunities to be active throughout the day, such as taking the stairs instead of the elevator, walking or cycling for transportation, or doing household chores and gardening.
Schedule It:
Treat physical activity like any other appointment and schedule it into your day. Set aside dedicated time for exercise and prioritize it as an essential part of self-care.
Be Flexible:
Be flexible with your exercise routine and adapt to changes in schedule or circumstances. If you can’t do your usual workout, find alternative activities or shorter bouts of exercise to stay active.
Conclusion:
Physical activity is a cornerstone of a healthy lifestyle, offering numerous benefits for physical, mental, and emotional well-being. By incorporating regular physical activity into your daily routine and following recommended guidelines for aerobic exercise, strength training, flexibility, and balance exercises, you can improve cardiovascular health, build strength and endurance, enhance mental health, and boost overall quality of life. Remember, every bit of movement counts, so find activities you enjoy and make physical activity a priority for lifelong health and vitality.
Physical Activity: The Key to Health and Well-being
Physical activity is a cornerstone of a healthy lifestyle, offering numerous benefits for physical, mental, and emotional well-being. From improving cardiovascular health and strengthening muscles to boosting mood and reducing stress, regular physical activity is essential for maintaining optimal health throughout life. In this comprehensive exploration, we will delve into the importance of physical activity, its various health benefits, recommended guidelines, types of activities, and strategies for incorporating physical activity into daily life.
Understanding the Importance of Physical Activity:
Physical activity encompasses any bodily movement produced by skeletal muscles that requires energy expenditure. It includes a wide range of activities, from structured exercise routines to everyday activities such as walking, gardening, and household chores. Regular physical activity is essential for overall health and well-being, as it contributes to:
Cardiovascular Health:
Physical activity strengthens the heart muscle, improves circulation, and reduces the risk of heart disease, stroke, and hypertension.
Musculoskeletal Health:
Weight-bearing and resistance exercises help build and maintain strong bones, muscles, and joints, reducing the risk of osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, and fractures.
Weight Management:
Physical activity helps control weight by burning calories and increasing metabolism, promoting fat loss and preserving lean muscle mass.
Mental Health:
Exercise releases endorphins, neurotransmitters that improve mood and reduce feelings of stress, anxiety, and depression. Regular physical activity is associated with better mental health outcomes and enhanced cognitive function.
Sleep Quality:
Physical activity can improve sleep quality and duration, leading to better overall sleep patterns and daytime alertness.
Energy Levels:
Regular physical activity boosts energy levels, reduces fatigue, and enhances overall vitality and stamina.
Recommended Guidelines for Physical Activity:
The World Health Organization (WHO) and various health organizations provide guidelines for physical activity to promote health and well-being. The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends the following:
Aerobic Exercise:
Adults should aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week. This can include activities such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, or dancing.
Strength Training:
Adults should engage in muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days per week, targeting major muscle groups with exercises such as weightlifting, resistance band exercises, or bodyweight exercises.
Flexibility and Balance Exercises:
Incorporating flexibility and balance exercises into your routine can help improve range of motion, prevent injuries, and enhance overall mobility and stability.
Types of Physical Activities:
Physical activities can be categorized into various types, each offering unique benefits for health and well-being:
Aerobic Exercise:
Aerobic activities, also known as cardio or endurance exercises, involve repetitive movements that increase heart rate and breathing rate, improving cardiovascular fitness and endurance. Examples include walking, running, cycling, swimming, and aerobic dance classes.
Strength Training:
Strength training, also known as resistance training or weightlifting, involves using resistance to build and maintain muscle strength, endurance, and mass. This can be done using free weights, weight machines, resistance bands, or bodyweight exercises such as push-ups, squats, and lunges.
Flexibility Exercises:
Flexibility exercises focus on improving joint range of motion and muscle flexibility, reducing the risk of injury and enhancing overall mobility and posture. Examples include stretching exercises, yoga, and Pilates.
Balance Exercises:
Balance exercises help improve stability, coordination, and proprioception, reducing the risk of falls and injuries, especially in older adults. Balance exercises may include standing on one leg, heel-to-toe walking, and Tai Chi.
Strategies for Incorporating Physical Activity into Daily Life:
Incorporating physical activity into daily life doesn’t have to be daunting. Simple strategies can help make physical activity a regular part of your routine:
Set Realistic Goals:
Set specific, achievable goals for physical activity, such as taking a daily walk, attending a fitness class, or completing a home workout routine.
Find Activities You Enjoy:
Choose physical activities that you enjoy and look forward to, whether it’s dancing, hiking, swimming, or playing a sport. Making exercise fun increases motivation and adherence.
Make It Social:
Exercise with friends, family members, or coworkers to make physical activity more enjoyable and social. Join group fitness classes, sports leagues, or outdoor recreational activities.
Incorporate Activity into Daily Routine:
Look for opportunities to be active throughout the day, such as taking the stairs instead of the elevator, walking or cycling for transportation, or doing household chores and gardening.
Schedule It:
Treat physical activity like any other appointment and schedule it into your day. Set aside dedicated time for exercise and prioritize it as an essential part of self-care.
Conclusion:
Physical activity is a vital component of a healthy lifestyle, offering numerous benefits for physical, mental, and emotional well-being. By incorporating regular physical activity into your daily routine and following recommended guidelines for aerobic exercise, strength training, flexibility, and balance exercises, you can improve cardiovascular health, build strength and endurance, enhance mental health, and boost overall quality of life. Remember every bit of movement counts, so find activities you enjoy and make physical activity a priority for lifelong health and vitality.