The Ultimate Guide to Health Screenings: Ensuring Your Well-being with Comprehensive Medical Evaluations
Introduction:
In the realm of healthcare, prevention is often hailed as the best medicine. Health screenings play a pivotal role in this preventive approach, serving as valuable tools for early detection, risk assessment, and intervention. From routine check-ups to specialized tests, health screenings provide individuals with crucial insights into their health status, enabling them to take proactive measures to safeguard their well-being. This comprehensive exploration delves into the importance, benefits, and key considerations of health screenings, highlighting their significance in promoting early detection, preventing diseases, and improving overall health outcomes.
Understanding Health Screenings:
Health screenings encompass a variety of tests and examinations aimed at assessing an individual’s health status, identifying risk factors, and detecting early signs of diseases or conditions. These screenings can target specific health concerns, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cancer, or infectious diseases, and may involve a range of methods, including blood tests, imaging studies, physical examinations, and questionnaires. Health screenings may be recommended based on factors such as age, gender, family history, lifestyle habits, and existing health conditions, with the goal of detecting health issues before they progress to more serious stages.
Importance of Health Screenings:
Health screenings are essential for several reasons, each underscored by the overarching goal of early detection and prevention. Firstly, screenings enable individuals to assess their current health status and identify any underlying health concerns that may require further evaluation or intervention. Early detection of diseases or risk factors allows for timely medical intervention, which can significantly improve treatment outcomes and prognosis. Moreover, health screenings empower individuals to take proactive steps to modify lifestyle behaviors, manage risk factors, and adopt preventive measures to minimize their risk of developing certain diseases or conditions.
Furthermore, health screenings play a crucial role in population health management by identifying trends, patterns, and disparities in health outcomes. By analyzing screening data at the population level, healthcare providers and public health authorities can identify high-risk groups, implement targeted interventions, and allocate resources more effectively to address prevalent health issues. Additionally, health screenings contribute to informed decision-making by providing individuals with the information they need to make choices about their health and healthcare, whether it involves seeking further evaluation, initiating treatment, or making lifestyle modifications.
Benefits of Health Screenings:
The benefits of health screenings are multifaceted and extend to individuals, healthcare providers, and society as a whole. Some key benefits include:
Early Detection and Treatment:
Health screenings can detect diseases or conditions at early stages when they are more easily treatable and may be associated with better treatment outcomes. Early intervention can help prevent disease progression, reduce complications, and improve overall health outcomes.
Prevention and Risk Reduction:
By identifying risk factors and health concerns early on, health screenings empower individuals to take proactive measures to mitigate their risk of developing certain diseases or conditions. This may involve lifestyle modifications, preventive medications, or targeted interventions aimed at reducing risk factors.
Improved Health Outcomes:
Regular health screenings can help individuals monitor their health status over time, track changes in risk factors or biomarkers, and assess the effectiveness of preventive measures or treatments. This ongoing monitoring allows for timely adjustments to healthcare plans, leading to improved health outcomes and quality of life.
Cost Savings:
Although health screenings may incur initial costs, they can result in significant cost savings in the long run by preventing or delaying the onset of diseases, reducing healthcare utilization, and minimizing the need for expensive treatments or interventions associated with advanced stages of illness.
Public Health Impact:
Health screenings contribute to population health by identifying prevalent health issues, monitoring disease trends, and informing public health policies and interventions. By addressing health concerns at the population level, screenings can help reduce the burden of disease, improve health equity, and enhance overall community well-being.
Key Considerations for Health Screenings:
While health screenings offer numerous benefits, it is essential to consider several key factors to ensure their effectiveness and appropriateness:
Evidence-Based Guidelines:
Health screenings should be conducted based on evidence-based guidelines established by reputable healthcare organizations and professional societies. These guidelines take into account factors such as age, gender, family history, and risk factors to determine the appropriate timing and frequency of screenings for various diseases or conditions.
Informed Decision-Making:
Individuals should be provided with comprehensive information about the purpose, benefits, risks, and limitations of health screenings to facilitate informed decision-making. This includes discussing the potential outcomes of screening tests, the implications of abnormal results, and the available treatment options or follow-up recommendations.
Individualized Approach:
Health screenings should be tailored to the individual’s unique health profile, including personal and family medical history, lifestyle habits, and preferences. A one-size-fits-all approach may not be suitable for everyone, and healthcare providers should consider individual circumstances when recommending screenings.
Follow-Up and Coordination of Care:
Abnormal screening results may require further evaluation, diagnostic testing, or medical interventions. It is essential to ensure timely follow-up and coordination of care to address any identified health concerns and facilitate appropriate treatment or management strategies.
Risk Communication and Counseling:
Effective risk communication and counseling are essential components of health screenings, particularly for tests with potential implications for individuals’ health and well-being. Healthcare providers should communicate screening results clearly, provide context about their significance, and offer guidance on next steps, including lifestyle modifications, preventive measures, or medical interventions.
Conclusion:
Health screenings are powerful tools for promoting early detection, prevention, and intervention in healthcare. By assessing individuals’ health status, identifying risk factors, and detecting early signs of diseases or conditions, screenings empower individuals to take proactive steps to safeguard their well-being and improve their overall health outcomes. Moreover, screenings contribute to population health management by identifying prevalent health issues, informing public health policies, and reducing the burden of disease on society. As part of a comprehensive approach to healthcare, health screenings play a crucial role in promoting a culture of prevention, wellness, and proactive healthcare management.
Introduction to Health Screenings
As an individual, it is crucial to prioritize your health and well-being. One of the most effective ways to do so is by undergoing regular health screenings. Health screenings play a vital role in detecting potential health issues at an early stage, enabling timely intervention and treatment. In this ultimate guide, I will walk you through the importance of health screenings, the key screenings for different age groups, the different types of screenings available, how to prepare for a screening, common misconceptions, the benefits of regular screenings, how to choose the right healthcare provider, and answer frequently asked questions. By the end of this guide, you will have a comprehensive understanding of health screenings and be empowered to take control of your health.
Importance of Health Screenings for Overall Well-being
Health screenings are an essential part of maintaining overall well-being. They act as preventive measures, allowing healthcare professionals to identify potential health risks before they manifest into more serious conditions. Regular screenings can detect diseases such as cancer, diabetes, heart disease, and high blood pressure in their early stages when treatment is most effective. By detecting these conditions early, health screenings can significantly increase the chances of successful treatment and improve the overall prognosis. Furthermore, health screenings provide an opportunity for healthcare providers to assess an individual’s overall health and offer guidance on lifestyle modifications to prevent future health issues.
Key Health Screenings for Different Age Groups
Health screenings can vary depending on an individual’s age and gender. Let’s explore some of the key screenings recommended for different age groups:
20s and 30s:
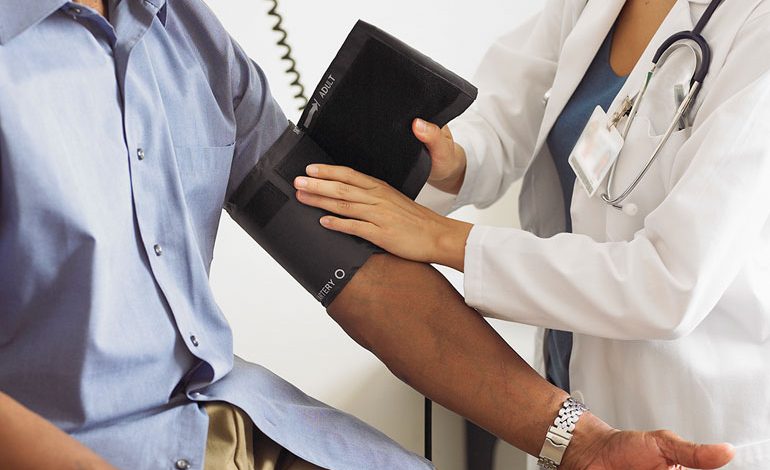
During this phase of life, it is important to focus on preventive measures. Regular screenings should include blood pressure measurements, cholesterol checks, and body mass index (BMI) assessments. Additionally, women in this age group should consider regular Pap smears and mammograms.
40s and 50s:
As individuals enter their 40s and 50s, the risk of developing certain health conditions increases. Screenings such as colonoscopies, bone density scans, and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests for men become crucial. Women should continue with mammograms and add regular screenings for osteoporosis.
60s and beyond:
In later years, health screenings become even more vital. Regular screenings should include colonoscopies, mammograms, bone density scans, prostate cancer screenings, and screenings for cardiovascular diseases.By following these age-appropriate screenings, individuals can stay ahead of potential health issues and ensure their well-being.
Understanding the Different Types of Health Screenings
Health screenings can encompass a wide range of tests and assessments. Here are some of the most common types of health screenings:
Blood Tests:
Blood tests are a fundamental part of health screenings. They provide valuable insights into an individual’s overall health by measuring various factors such as cholesterol levels, blood sugar levels, liver function, kidney function, and hormone levels. These tests can help detect conditions like diabetes, high cholesterol, liver disease, and hormonal imbalances.
Imaging Tests:
Imaging tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, are used to visualize the internal structures of the body. These tests can help identify abnormalities, such as tumors, fractures, or organ damage. Imaging tests are particularly useful in detecting conditions like cancer, heart disease, and bone disorders.
Physical Examinations:
Physical examinations involve a thorough assessment of an individual’s overall health. Healthcare providers check vital signs, perform a visual examination, and may conduct specific tests based on the individual’s age and risk factors. Physical examinations can help identify potential health issues and guide further screenings or interventions.
Genetic Testing:
Genetic testing involves analyzing an individual’s DNA to identify genetic variations or mutations that may increase the risk of certain diseases. This type of screening is particularly useful for individuals with a family history of genetic disorders or those who want to assess their risk for hereditary conditions.By understanding the different types of health screenings, individuals can make informed decisions about their healthcare and ensure comprehensive evaluations of their well-being.
Preparing for a Health Screening
Proper preparation is essential for a successful health screening. Here are some general guidelines to follow:
Schedule an appointment:
Contact your healthcare provider to schedule a health screening appointment. Discuss any specific instructions or requirements beforehand.
Provide accurate information:
When scheduling the appointment, be prepared to provide your medical history, current medications, and any existing health conditions. This information will help healthcare providers tailor the screenings to your specific needs.
Fasting requirements:
Some screenings, such as cholesterol tests or blood glucose tests, may require fasting for a certain period beforehand. Follow the fasting instructions provided by your healthcare provider to ensure accurate results.
Dress comfortably:
Wear loose-fitting clothing that allows easy access to your arms for blood pressure measurements and blood draws. Avoid wearing jewelry or accessories that may interfere with the screenings.
Bring necessary documentation:
Carry any relevant medical documents, such as previous test results or medical records, to the screening appointment. This information can help healthcare providers compare current and past results for a more accurate assessment. By following these preparation guidelines, you can ensure a smooth and efficient health screening experience.
Common Misconceptions About Health Screenings
There are several common misconceptions surrounding health screenings that can hinder individuals from seeking these important evaluations. Let’s address some of these misconceptions and provide clarity:Feeling fine does not guarantee that there are no underlying health issues. Many conditions, such as high blood pressure or early-stage cancer, are asymptomatic in their initial stages. Regular health screenings can detect these conditions before symptoms arise, increasing the chances of successful treatment.
Screenings are only necessary for older individuals:
Health screenings are important for individuals of all ages. Some conditions, like certain types of cancer, can occur at any age. Additionally, screenings in younger individuals can help establish baseline measurements and identify potential risk factors for future health issues.
I can rely solely on self-screening:
Self-screening, such as performing breast or testicular self-exams, is a valuable practice. However, it should not replace regular screenings conducted by healthcare professionals. Healthcare providers have the expertise and tools to detect potential issues that may not be apparent during self-screening.By dispelling these misconceptions, individuals can better understand the necessity and benefits of health screenings.
Benefits of Regular Health Screenings
Regular health screenings offer numerous benefits for individuals of all ages. Here are some key advantages:
Early detection and treatment:
Regular screenings can detect potential health issues at an early stage, when treatment is most effective. This can significantly improve the prognosis and increase the chances of successful treatment.
Prevention and intervention:
Screenings enable healthcare providers to identify risk factors and offer guidance on preventive measures. Lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes or exercise routines, can help prevent future health issues.
Peace of mind:
Knowing that you are taking proactive steps to monitor your health can provide peace of mind. Regular screenings can alleviate anxiety and enable individuals to feel more in control of their well-being.
Cost savings:
Early detection of health issues can lead to less expensive and less invasive treatments. By avoiding advanced stages of diseases, individuals can potentially save on medical expenses.
By prioritizing regular health screenings, individuals can reap these benefits and lead healthier lives.
How to Choose the Right Healthcare Provider for Health Screenings
Choosing the right healthcare provider for health screenings is crucial to ensure accurate assessments and quality care. Here are some factors to consider:
Expertise and qualifications:
Research the healthcare provider’s qualifications, experience, and expertise in conducting health screenings. Look for certifications or affiliations that demonstrate their knowledge in the field.
Reputation and reviews:
Read reviews and seek recommendations from trusted sources to gauge the reputation of the healthcare provider. Positive testimonials and feedback from previous patients can indicate a reliable and trustworthy provider.
Accessibility and convenience:
Consider the location, availability, and accessibility of the healthcare provider’s facility. Opt for a provider who offers convenient appointment scheduling and is easily accessible in case of emergencies or follow-up visits.
Communication and rapport:
Effective communication and a good rapport with your healthcare provider are essential for a positive screening experience. Choose a provider who listens attentively, addresses your concerns, and provides clear explanations.
Insurance coverage:
Check if the healthcare provider accepts your insurance plan to ensure affordable screenings. Inquire about any out-of-pocket costs or payment options beforehand.By considering these factors, individuals can make an informed decision when selecting a healthcare provider for their health screenings.
Frequently Asked Questions About Health Screenings
When should I start getting regular health screenings?
The age to start regular health screenings may vary depending on the type of screening and individual risk factors. It is best to consult with your healthcare provider to determine when you should begin.
How often should I undergo health screenings?
The frequency of health screenings depends on various factors, including age, gender, and individual health status. Healthcare providers can provide personalized recommendations based on these factors.
What if a health screening detects an abnormality?
If a health screening detects an abnormality, further diagnostic tests may be necessary to confirm the condition. Your healthcare provider will guide you through the next steps, which may include additional tests, consultations with specialists, or treatment plans.
Are health screenings covered by insurance?
Many health insurance plans cover preventive health screenings. However, coverage may vary depending on the specific plan. It is advisable to check with your insurance provider to understand the extent of coverage for health screenings.
Can I request specific health screenings?
Yes, you can discuss specific health screenings with your healthcare provider based on your concerns, family history, or risk factors. Your healthcare provider will consider your requests and assess their appropriateness based on current medical guidelines.These are just a few of the frequently asked questions regarding health screenings. It is always recommended to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized and accurate information.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Health with Comprehensive Medical Evaluations
In conclusion;
Health screenings are a vital component of maintaining overall well-being. By undergoing regular screenings, individuals can detect potential health issues at an early stage, enabling early intervention and treatment. Understanding the different types of screenings, preparing adequately, dispelling common misconceptions, and choosing the right healthcare provider are essential steps in taking control of your health. By prioritizing regular health screenings, individuals can ensure their well-being and enjoy a healthier future. Don’t wait any longer – schedule your health screening today and empower yourself to live a healthier life.CTA: Take charge of your health by scheduling your next health screening today. Contact your healthcare provider and prioritize your well-being. Your future self will thank you.
Early Detection and Treatment: The Cornerstone of Effective Healthcare
Introduction:
Early detection and treatment of diseases are fundamental pillars of modern healthcare systems. By identifying health conditions in their early stages, healthcare providers can intervene promptly, mitigate disease progression, and improve patient outcomes. Early detection enables individuals to access timely medical care, receive appropriate treatments, and adopt preventive measures to minimize the impact of illness on their health and well-being. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the importance, benefits, and strategies for early detection and treatment, highlighting their critical role in promoting health, preventing disease, and saving lives.
The Importance of Early Detection:
Early detection of diseases is crucial for several reasons, each underscored by the overarching goal of improving patient outcomes and quality of life. Firstly, early detection allows healthcare providers to identify health conditions before they progress to advanced stages, when symptoms may be more severe and treatment options may be limited. By detecting diseases early, healthcare providers can implement timely interventions, initiate appropriate treatments, and prevent or delay complications associated with advanced disease states.
Moreover, early detection provides individuals with the opportunity to take proactive measures to manage their health and mitigate disease risks. Whether through lifestyle modifications, preventive medications, or regular monitoring, individuals can adopt strategies to reduce their risk of developing certain diseases or conditions and optimize their overall health outcomes. Additionally, early detection can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their healthcare, seek appropriate medical care, and engage in shared decision-making with their healthcare providers.
Benefits of Early Detection and Treatment:
The benefits of early detection and treatment are multifaceted and extend to individuals, healthcare systems, and society as a whole. Some key benefits include:
Improved Treatment Outcomes:
Early detection enables healthcare providers to intervene when diseases are at their most treatable stages, often resulting in better treatment outcomes and prognosis. For many diseases, such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and infectious diseases, early detection is associated with higher survival rates, reduced morbidity, and improved quality of life for affected individuals.
Reduced Healthcare Costs:
Early detection and treatment can lead to significant cost savings for healthcare systems by preventing or delaying the onset of diseases, reducing the need for expensive treatments or interventions, and minimizing healthcare utilization associated with advanced disease states. By investing in early detection and preventive care, healthcare systems can achieve long-term cost efficiencies and allocate resources more effectively to address other healthcare priorities.
Prevention of Disease Progression:
Early detection enables healthcare providers to identify risk factors, implement preventive measures, and intervene before diseases progress to more advanced stages. By addressing health conditions early, healthcare providers can prevent or delay disease progression, reduce complications, and improve overall health outcomes for affected individuals.
Public Health Impact:
Early detection plays a crucial role in public health by identifying prevalent health issues, monitoring disease trends, and informing targeted interventions and public health policies. By addressing health concerns at the population level, early detection initiatives can help reduce the burden of disease, improve health equity, and enhance overall community well-being.
Empowerment and Engagement:
Early detection empowers individuals to take control of their health, seek appropriate medical care, and engage in proactive healthcare management. By providing individuals with the information and resources they need to make informed decisions about their health, early detection initiatives promote health literacy, self-efficacy, and patient engagement in their healthcare journey.
Strategies for Early Detection and Treatment:
Effective early detection and treatment strategies require a multifaceted approach that encompasses various components, including:
Screening Programs:
Screening programs aim to detect diseases or risk factors in asymptomatic individuals through systematic testing, examinations, or assessments. These programs may target specific populations based on age, gender, family history, or lifestyle factors and typically involve evidence-based screening tests, such as mammograms, colonoscopies, and blood tests.
Risk Assessment and Risk Stratification:
Risk assessment tools and algorithms help healthcare providers evaluate individuals’ risk factors for certain diseases or conditions and identify those who may benefit from early detection measures. By stratifying individuals based on their risk profiles, healthcare providers can tailor screening recommendations and preventive interventions to optimize health outcomes.
Public Health Campaigns and Education:
Public health campaigns and education initiatives raise awareness about the importance of early detection and treatment, promote health screenings and preventive measures, and empower individuals to take proactive steps to safeguard their health. These campaigns may utilize various communication channels, such as mass media, social media, community events, and educational materials, to reach diverse audiences and promote health literacy.
Integration of Technology:
Advances in technology, such as electronic health records, telemedicine, and digital health platforms, have the potential to revolutionize early detection and treatment efforts by facilitating remote monitoring, real-time data collection, and personalized healthcare interventions. By leveraging technology, healthcare providers can enhance access to care, improve care coordination, and empower individuals to actively participate in their healthcare management.
Collaborative Care Models:
Collaborative care models involve multidisciplinary teams of healthcare providers working together to deliver comprehensive, coordinated, and patient-centered care. By fostering collaboration among primary care providers, specialists, nurses, pharmacists, and other healthcare professionals, these models ensure timely access to appropriate interventions, streamline care delivery processes, and optimize health outcomes for individuals with complex health needs.
Conclusion:
Early detection and treatment are essential components of effective healthcare delivery, with far-reaching benefits for individuals, healthcare systems, and society as a whole. By identifying health conditions in their early stages, healthcare providers can intervene promptly, mitigate disease progression, and improve patient outcomes. Moreover, early detection empowers individuals to take proactive measures to manage their health, mitigate disease risks, and optimize their overall well-being. As healthcare systems continue to evolve, early detection and treatment initiatives will remain critical priorities for promoting health, preventing disease, and saving lives.