Fitness for Older Adults: Embracing Health and Vitality at Every Age

Introduction:
As the saying goes, age is just a number – and when it comes to fitness, this adage couldn’t be more accurate. While physical activity may seem daunting for older adults due to concerns about safety and limitations, staying active is not only feasible but also crucial for maintaining health, mobility, and independence as we age. In fact, regular exercise offers a multitude of benefits for older adults, ranging from improved strength and balance to enhanced mental well-being and quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the importance of fitness for older adults, debunk common myths, and provide practical tips for starting and maintaining an exercise routine tailored to individual needs and abilities.
The Importance of Fitness for Older Adults:
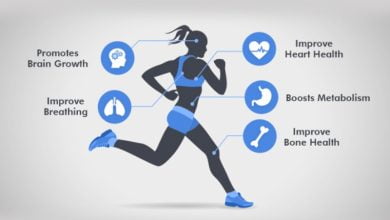
Physical activity plays a pivotal role in healthy aging by preserving muscle mass, bone density, and flexibility, while also reducing the risk of chronic diseases and age-related conditions. Regular exercise can help older adults maintain or improve cardiovascular health, manage weight, and lower the risk of hypertension, diabetes, and osteoporosis. Furthermore, staying active promotes mental acuity, reduces the risk of depression and anxiety, and enhances overall quality of life.Engaging in regular exercise also fosters independence and functional ability, enabling older adults to perform daily activities with ease and confidence. Strength training, in particular, is crucial for maintaining muscle strength and preventing falls, which are a leading cause of injury and disability among older adults. By incorporating a variety of exercises into their routine, older adults can improve balance, coordination, and proprioception, reducing the risk of falls and enhancing mobility and stability.
Debunking Common Myths About Exercise and Aging:
Despite the numerous benefits of exercise, there are several misconceptions surrounding physical activity and aging that may deter older adults from embracing an active lifestyle. One common myth is that it’s too late to start exercising or make significant improvements in fitness later in life. However, research has shown that older adults can experience substantial gains in strength, endurance, and flexibility with regular exercise, regardless of age or fitness level. Moreover, the benefits of exercise extend far beyond physical health, positively impacting cognitive function, mood, and overall well-being.Another myth is that exercise is inherently risky for older adults and may exacerbate existing health conditions or lead to injury. While it’s essential for older adults to exercise caution and consult with a healthcare professional before starting a new exercise program, most individuals can safely engage in physical activity with proper guidance and modifications. In fact, regular exercise can help manage chronic conditions
such as arthritis, heart disease, and osteoporosis, improving symptoms and reducing the need for medication.
Tips for Starting and Maintaining an Exercise Routine:
Starting an exercise routine can seem overwhelming, especially for older adults who may be unfamiliar with fitness or have physical limitations. However, with the right approach and mindset, getting active can be both enjoyable and rewarding. Here are some tips for older adults looking to embark on a fitness journey:
Consult with a healthcare professional:
Before starting any new exercise program, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to assess individual health status and any potential risks or contraindications.
Start slow and gradually progress:
Begin with low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, or tai chi, and gradually increase the intensity, duration, and frequency of exercise as fitness improves.
Focus on strength and balance:
Incorporate strength training exercises using resistance bands, free weights, or bodyweight exercises to build muscle strength and improve balance and stability.
Stay consistent:
Consistency is key to seeing results and reaping the benefits of exercise. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with two or more days of strength training exercises.
Listen to your body:
Pay attention to how your body feels during and after exercise, and adjust intensity or duration as needed to avoid overexertion or injury. It’s essential to prioritize safety and listen to any warning signs such as pain, dizziness, or shortness of breath.
Find activities you enjoy:
Choose activities that you genuinely enjoy and look forward to, whether it’s dancing, gardening, cycling, or participating in group fitness classes. Making exercise fun and engaging increases the likelihood of sticking with it long term.
Stay social:
Exercise doesn’t have to be a solitary activity. Joining a walking group, fitness class, or recreational sports team provides social support and motivation, making exercise more enjoyable and sustainable.
Prioritize recovery:
Allow time for rest and recovery between workouts, and incorporate activities like stretching, yoga, or foam rolling to improve flexibility and prevent injury.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fitness is a journey that transcends age, and it’s never too late to reap the benefits of regular exercise. For older adults, staying active is paramount for maintaining health, mobility, and independence well into the golden years. By debunking common myths about
exercise and aging and adopting a positive mindset, older adults can embrace physical activity as a means of enhancing overall well-being and quality of life. With the guidance of healthcare professionals and the support of friends and family, older adults can embark on a fitness journey tailored to their individual needs and abilities, embracing health and vitality at every stage of life.
Consulting with a Healthcare Professional: The Cornerstone of Personal Health and Wellness
In a world where health information is readily available at our fingertips, the importance of consulting with a healthcare professional cannot be overstated. Whether seeking medical advice, managing chronic conditions, or embarking on a new health journey, the guidance and expertise of a qualified healthcare professional serve as invaluable resources for ensuring optimal health and well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the significance of consulting with a healthcare professional, explore the benefits of establishing a collaborative relationship, and provide practical tips for making the most of healthcare appointments.
The Importance of Consulting with a Healthcare Professional:
Consulting with a healthcare professional forms the foundation of proactive healthcare management and disease prevention. Healthcare professionals, including physicians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and specialists, possess specialized knowledge and training to assess, diagnose, and treat a wide range of health conditions. Whether addressing acute illnesses, managing chronic diseases, or providing preventive care, healthcare professionals play a vital role in guiding individuals toward better health outcomes.One of the primary benefits of consulting with a healthcare professional is access to personalized medical advice tailored to individual needs and circumstances. Healthcare professionals take into account factors such as medical history, lifestyle, family history, and risk factors when formulating treatment plans and recommendations. This personalized approach enables individuals to receive targeted interventions and interventions that address their specific health concerns, leading to more effective outcomes.Moreover, healthcare professionals serve as advocates for their patients, advocating for their rights, preferences, and well-being within the healthcare system. They help individuals navigate complex medical decisions, understand treatment options, and access necessary resources and support services. By fostering open communication and trust, healthcare professionals empower individuals to actively participate in their healthcare journey and make informed decisions about their health.
Establishing a Collaborative Relationship
Building a collaborative relationship with a healthcare professional is essential for maximizing the benefits of medical care and promoting continuity of care. A collaborative approach involves open communication, mutual respect, and shared decision-making between patients
healthcare providers. By working together as partners in health, individuals and healthcare professionals can address health concerns comprehensively and develop effective strategies for achieving health goals.Effective communication is a cornerstone of a collaborative relationship between patients and healthcare professionals. Individuals should feel comfortable discussing their health concerns, asking questions, and expressing their preferences and values. Likewise, healthcare professionals should listen attentively, validate patient experiences, and provide clear and concise explanations of medical information and treatment options. Creating a supportive and nonjudgmental environment encourages honest dialogue and fosters trust between patients and providers.In addition to communication, mutual respect and trust are essential components of a collaborative relationship. Healthcare professionals should respect patients’ autonomy, preferences, and cultural beliefs, recognizing them as partners in the decision-making process. Conversely, patients should trust their healthcare providers’ expertise, experience, and recommendations, understanding that they have their best interests at heart. Establishing mutual respect and trust lays the groundwork for a positive and productive partnership focused on achieving optimal health outcomes.
Practical Tips for Making the Most of Healthcare Appointments
To make the most of healthcare appointments and optimize the quality of care received, individuals can adopt several strategies for effective communication and preparation. Here are some practical tips for maximizing healthcare appointments:
Prepare in advance:
Before the appointment, write down any symptoms, concerns, or questions you have, as well as relevant medical history, medications, and allergies. Bringing a list of prepared questions ensures that important topics are addressed during the appointment.
Be honest and forthcoming:
Provide accurate and detailed information about your health status, including symptoms, lifestyle habits, and any recent changes or developments. Open and honest communication allows healthcare professionals to make informed assessments and recommendations.
Actively participate:
Take an active role in the appointment by asking questions, seeking clarification, and expressing your preferences and concerns. Don’t hesitate to advocate for yourself and request further explanation or alternative options if needed.
Seek clarification:
If you don’t understand something your healthcare provider says, don’t hesitate to ask for clarification or additional information. Healthcare professionals are committed to ensuring that patients have a clear understanding of their health conditions and treatment plans.
Follow through with recommendations:
After the appointment, follow through with any recommendations or treatment plans discussed with your healthcare provider. This may include scheduling follow-up appointments, undergoing diagnostic tests, starting or adjusting medications, or making lifestyle changes.
Keep lines of communication open:
Maintain ongoing communication with your healthcare provider between appointments, especially if you experience any new symptoms, side effects, or concerns. Promptly reporting changes in your health status allows for timely adjustments to treatment plans and interventions.
Stay informed:
Stay informed about your health condition, treatment options, and preventive measures by accessing reliable sources of health information. However, be cautious of misinformation and seek guidance from trusted healthcare professionals when evaluating medical advice or recommendations.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for promoting personal health and wellness throughout the lifespan. By establishing a collaborative relationship built on effective communication, mutual respect, and trust, individuals can receive personalized medical advice and guidance tailored to their unique needs and circumstances. By actively participating in their healthcare journey and following through with recommendations, individuals can empower themselves to achieve optimal health outcomes and enhance their overall quality of life. By recognizing the importance of consulting with a healthcare professional and prioritizing proactive healthcare management, individuals can take proactive steps towards achieving and maintaining health and well-being.
Establishing a Collaborative Relationship: Enhancing Healthcare Outcomes Through Partnership:
In the realm of healthcare, the concept of establishing a collaborative relationship between patients and healthcare providers has gained increasing recognition as a fundamental component of high-quality care. A collaborative relationship emphasizes partnership, open communication, mutual respect, and shared decision-making between patients and healthcare professionals. By working together as partners in health, individuals and healthcare providers can optimize healthcare outcomes, improve patient satisfaction, and promote overall well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the importance of establishing a collaborative relationship in healthcare, discuss key principles and strategies for fostering collaboration, and highlight the benefits of a patient-centered approach to care.
The Importance of Establishing a Collaborative Relationship:
Establishing a collaborative relationship between patients and healthcare providers is essential for delivering patient-centered care and achieving positive health outcomes. Traditionally, healthcare delivery has been characterized by a hierarchical model in which healthcare providers assume primary decision-making authority, while patients play a passive role in their care. However, this paternalistic approach has increasingly been replaced by a collaborative model that recognizes patients as active participants in their healthcare journey.One of the primary benefits of a collaborative relationship is improved communication between patients and healthcare providers. Effective communication involves not only the exchange of information but also active listening, empathy, and understanding. By fostering open communication and creating a supportive environment, patients feel empowered to voice their concerns, ask questions, and express their preferences and values. In turn, healthcare providers can provide tailored medical advice, address patient needs and concerns, and involve patients in shared decision-making.Moreover, a collaborative relationship promotes patient engagement and empowerment by involving patients in the decision-making process regarding their healthcare. Rather than passively receiving instructions from healthcare providers, patients become active participants in decisions related to treatment options, care plans, and lifestyle modifications. This sense of ownership and autonomy enhances patient satisfaction, adherence to treatment regimens, and overall health outcomes.Furthermore, a collaborative relationship fosters mutual respect and trust between patients and healthcare providers. Patients feel valued and respected as partners in their care, while healthcare providers recognize patients as individuals with unique needs, preferences, and goals. This mutual respect forms the foundation of a positive and productive partnership focused on achieving optimal health outcomes and promoting overall well-being.
Key Principles and Strategies for Fostering Collaboration
Several key principles and strategies can help healthcare providers establish and maintain a collaborative relationship with their patients:
Patient-Centered Care:
Prioritize the needs, preferences, and values of the patient when developing care plans and making healthcare decisions. Take into account individual circumstances, cultural beliefs, and personal goals to provide personalized and patient-centered care.
Open Communication:
Create a supportive and nonjudgmental environment that encourages patients to communicate openly and honestly about their health concerns, symptoms, and treatment preferences. Listen attentively, validate patient experiences, and provide clear and concise explanations of medical information and treatment options.
Shared Decision-Making:
Involve patients in the decision-making process by presenting information about treatment options, risks, benefits, and alternatives in a clear and understandable manner. Collaborate with patients to develop care plans that align with their goals, values, and preferences, ensuring informed decision-making and active participation in healthcare.
Respect for Patient Autonomy:
Respect patients’ autonomy and right to make healthcare decisions based on their own values and beliefs. Avoid paternalistic attitudes and involve patients in decisions about their care, empowering them to take an active role in managing their health.
Cultural Competence:
Recognize and respect cultural differences and diversity among patients, including language, beliefs, customs, and traditions. Culturally competent care involves understanding and addressing the unique needs and preferences of diverse patient populations, fostering trust and rapport in the patient-provider relationship.
Empathy and Compassion:
Demonstrate empathy, compassion, and understanding toward patients, acknowledging the emotional and psychological aspects of illness and healthcare experiences. Show genuine concern for patients’ well-being, validate their emotions, and provide emotional support throughout the care process.
Collaborative Care Planning:
Collaborate with interdisciplinary healthcare team members, including nurses, specialists, therapists, and social workers, to coordinate comprehensive and holistic care for patients. Engage in care planning discussions, share relevant information, and ensure continuity of care across healthcare settings and providers.
Benefits of a Patient-Centered Approach to Care:
Embracing a patient-centered approach to care has numerous benefits for both patients and healthcare providers:
Improved Patient Satisfaction:
Patients report higher levels of satisfaction with their care when they feel respected, heard, and involved in decisions about their health. A patient-centered approach enhances the overall care experience and fosters positive relationships between patients and healthcare providers.
Enhanced Health Outcomes:
Collaborative care promotes better health outcomes by addressing patients’ unique needs, preferences, and goals. Patients are more likely to adhere to treatment regimens, follow preventive measures, and engage in healthy behaviors when they feel actively involved in their care.
Increased Adherence to Treatment:
Patients are more likely to adhere to treatment recommendations and follow-up appointments when they understand the rationale behind their care plan and actively participate in decision-making. Shared decision-making promotes treatment adherence and patient engagement in self-management activities.
Reduced Healthcare Disparities:
A patient-centered approach helps address healthcare disparities by recognizing and respecting the diverse needs and preferences of patients from different backgrounds and communities. Culturally competent care promotes equity and access to quality healthcare for all patients.
Enhanced Provider Satisfaction:
Healthcare providers report greater job satisfaction and fulfillment when they are able to establish meaningful connections with their patients and deliver personalized, patient-centered care. Collaborative relationships enhance job satisfaction and reduce burnout among healthcare professionals.
Optimized Resource Utilization:
Collaborative care promotes efficient use of healthcare resources by focusing on preventive measures, early intervention, and patient education. By addressing patients’ needs and concerns proactively, healthcare providers can prevent complications, reduce hospitalizations, and minimize healthcare costs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, establishing a collaborative relationship between patients and healthcare providers is essential for delivering high-quality, patient-centered care. By fostering open communication, mutual respect, and shared decision-making, healthcare professionals can empower patients to take an active role in their healthcare journey and achieve optimal health outcomes. A patient-centered approach enhances patient satisfaction, adherence to treatment, and overall well-being, while also promoting equity and access to quality healthcare for all individuals. By embracing collaboration and partnership in healthcare delivery, patients and providers can work together to promote health, prevent disease, and enhance the quality of life for all.
Patient-Centered Care: Empowering Patients, Enhancing Healthcare:
In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, one concept has emerged as a cornerstone of quality care: patient-centered care. Rooted in the principles of respect, empathy, and collaboration, patient-centered care places patients at the forefront of their healthcare experience, empowering them to actively participate in decision-making, set goals, and take charge of their well-being. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the essence of patient-centered care, discuss its fundamental principles, highlight its benefits for patients and healthcare providers, and provide practical insights for implementing patient-centered practices in healthcare settings.
Understanding Patient-Centered Care:
At its core, patient-centered care is a philosophy that prioritizes the needs, preferences, and values of patients in the delivery of healthcare services. It shifts the focus from treating diseases and symptoms to caring for the whole person – mind, body, and spirit. Patient-centered care recognizes that each patient is unique, with their own set of beliefs, experiences, and goals, and emphasizes the importance of tailoring care to meet individual needs and preferences.
Key elements of patient-centered care include:
Respect and Dignity:
Patients are treated with respect, dignity, and compassion, regardless of their background, beliefs, or health status. Healthcare providers listen attentively, validate patient experiences, and involve them in decision-making processes.
Empathy and Compassion:
Healthcare providers demonstrate empathy and compassion toward patients, acknowledging their emotions, fears, and concerns. They strive to understand the patient’s perspective and provide emotional support throughout the care journey.
Partnership and Collaboration:
Patients are viewed as partners in their care, actively participating in decision-making processes and care planning discussions. Healthcare providers collaborate with patients to develop care plans that align with their goals, values, and preferences.
Information Sharing and Transparency:
Patients are provided with clear and understandable information about their health condition, treatment options, and care plan. Healthcare providers communicate openly and transparently, ensuring that patients are well-informed and empowered to make informed decisions about their health.
Holistic Approach:
Patient-centered care takes a holistic approach to health and well-being, addressing not only physical symptoms but also emotional, social, and spiritual needs. Healthcare providers consider the patient’s overall well-being and quality of life when developing care plans.
Benefits of Patient-Centered Care:
Patient-centered care offers a multitude of benefits for patients, healthcare providers, and healthcare systems alike:
Improved Patient Satisfaction:
Patients report higher levels of satisfaction with their care when they feel heard, respected, and involved in decision-making processes. Patient-centered care enhances the overall care experience and fosters positive relationships between patients and healthcare providers.
Enhanced Health Outcomes:
Patients who receive patient-centered care experience better health outcomes, including improved adherence to treatment regimens, reduced hospitalizations, and enhanced quality of life. Patient engagement and empowerment lead to more effective self-management of chronic conditions and preventive healthcare behaviors.
Increased Adherence to Treatment:
Patients are more likely to adhere to treatment recommendations and follow-up appointments when they feel actively involved in their care. Patient-centered care promotes shared decision-making, allowing patients to make informed choices about their treatment options based on their values and preferences.
Reduced Healthcare Disparities:
Patient-centered care helps address healthcare disparities by recognizing and respecting the diverse needs and preferences of patients from different backgrounds and communities. Culturally competent care promotes equity and access to quality healthcare for all individuals, regardless of race, ethnicity, or socioeconomic status.
Enhanced Provider Satisfaction:
Healthcare providers experience greater job satisfaction and fulfillment when they are able to establish meaningful connections with their patients and deliver personalized, patient-centered care. Collaborative relationships with patients enhance provider satisfaction and reduce burnout in healthcare professionals.
Optimized Resource Utilization:
Patient-centered care promotes efficient use of healthcare resources by focusing on preventive measures, early intervention, and patient education. By addressing patients’ needs and concerns proactively, healthcare providers can prevent complications, reduce hospitalizations, and minimize healthcare costs.
Implementing Patient-Centered Care Practices:
Implementing patient-centered care practices requires a commitment to culture change and continuous improvement within healthcare organizations. Here are some practical strategies for incorporating patient-centered care principles into healthcare delivery:
Educate and Train Healthcare Providers:
Provide education and training to healthcare providers on the principles and importance of patient-centered care. Offer workshops, seminars, and continuing education programs to enhance communication skills, cultural competence, and empathy.
Empower Patients Through Education:
Educate patients about their rights, responsibilities, and the importance of active participation in their healthcare. Provide information and resources to help patients make informed decisions about their health and engage in self-management activities.
Promote Shared Decision-Making:
Encourage healthcare providers to involve patients in decision-making processes and care planning discussions. Use decision aids, informational materials, and shared decision-making tools to facilitate informed choices and collaborative decision-making.
Create Supportive Environments:
Design healthcare environments that promote comfort, privacy, and open communication between patients and healthcare providers. Foster a culture of respect, empathy, and compassion throughout the organization, from frontline staff to senior leadership.
Collect and Use Patient Feedback:
Solicit feedback from patients about their care experiences through surveys, focus groups, and patient advisory councils. Use patient feedback to identify areas for improvement and implement changes to enhance patient-centered care delivery.
Measure and Monitor Outcomes:
Establish metrics and benchmarks for assessing the quality and effectiveness of patient-centered care initiatives. Monitor patient satisfaction scores, health outcomes, and healthcare utilization data to evaluate the impact of patient-centered care practices and identify opportunities for improvement.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, patient-centered care represents a paradigm shift in healthcare delivery, placing patients at the forefront of their care experience and empowering them to actively participate in decision-making processes. By prioritizing respect, empathy, collaboration, and transparency, patient-centered care enhances patient satisfaction, improves health outcomes, and fosters positive relationships between patients and healthcare providers. Implementing patient-centered care practices requires a commitment to culture change, education, and continuous improvement within healthcare organizations. By embracing patient-centered care principles and practices, healthcare providers can create environments that promote patient empowerment, engagement, and well-being, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and a higher quality of care for all.